Apple’s Software Patents
Apple's software-based patents have become a focal point of admiration in the tech industry. As one of the most influential businesses in the field, Apple's innovations in software development have both reshaped the digital landscape and sparked debates surrounding intellectual property (IP) and patent practices.
Apple boasts an extensive IP portfolio, including 100 software and operating system-related patents obtained during the past five years (GreyB). From user interface designs to algorithms powering intelligent assistants, Apple's IP protections cover a wide array of technological innovations. For example, Apple’s Vision Pro has “required over a staggering 5,000 patents to make the Apple Vision Pro a reality” (O'Neill). The Apple Vision Pro is described as “a head-mounted device having a plurality of electrodes configured to detect optical events (Azemi et al.).” Businesses, like Apple, have strategies when developing their IP portfolios. People can study larger companies’ IP portfolio, like Apple, to answer “the question of optimal IP policy” (Boudreau et al.).
Companies, when developing their IP portfolio, need to balance formal IP protections and trade secrets. There are tradeoffs for both IP protections and trade secrets. Protection applications through patents will expose the information to the public. Exposed information could negatively impact the business. Trade secrets will keep that information private and limit what competitors know. Patents, as a whole, “is becoming increasingly important for strategic management as innovation shifts to digital platforms” (Boudreau et al.). Knowing when to and when not to apply for patent protection will provide a competitive advantage. Effective strategies to decide between patent protections and trade secrets help maintain a competitive advantage. An analysis of a competitor’s IP portfolio could reveal sensitive information and help with more competitive advantages.
Businesses “owning software patents is crucial for market operations and for seeking strategic benefits in market competition” (Kwon and Marco). “The software sector is one of the ‘complex technology’ areas where innovation is created cumulatively and patent enforcement is effective for market competition” (Kwon and Marco). “Software patents can also give you a competitive advantage and increase the odds of acquisition by a larger company” (Rapacke 2020). Patents clearly help add value to businesses. Patents have strategic and economic advantages.
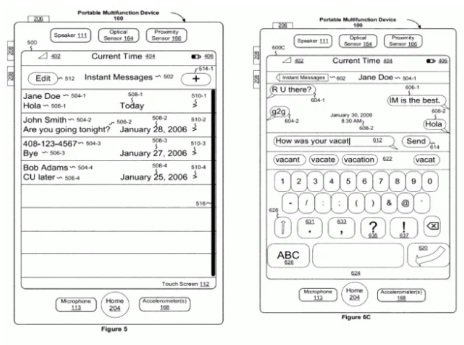
Figure 1
Not all Apple patents are for ground-breaking, industry-defining inventions. Patent Number 20190102924 is a patent granted to Apple in 2020 for generating synthetic group selfies. Synthetic group selfies allow the usage of individual selfies to create a single, new group image. Figure 3 is an image submitted by Apple in its application for Patent Number 20190102924 to explain its technology. Figure 3 is a solution to a problem that already has many alternatives, like photoshop.
Apple’s long-standing legal dispute with their competitor Samsung is far too complex to effectively analyze here. The Apple vs. Android saga is in regards to smartphone and tablet technology. However, the Apple vs. Android patent litigation illustrates the immense importance of patents along with their potential implications for the broader tech industry (Graziano). In April 2011, Apple filed its first claim against Samsung in the US District Court for the Northern District of California in San Jose, California. Subsequently, Apple filed similar cases against Samsung in several countries worldwide. Samsung filed many countersuits against Apple. The two tech companies finally reached an out-of-court settlement in the United States in 2018. Apple vs Android helps explain the global impacts of effective IP portfolios.
In summary, Apple has an extensive IP portfolio similar to other large tech companies. With thousands of patents, companies and competitors can study Apple’s IP portfolio to gain competitive advantages. Protections through patents needs to follow a strategy to maximize effectiveness. Companies, like Apple, balance formal IP protections and trade secrets to maintain competitive advantages. Patents offer strategic and economic benefits, enhance market competition, and can increase acquisition chances by larger companies.
Figure 1 shows an example of one of Apple’s patents, Patent Number 8223134. It is a patent granted to Apple in 2012 for a “portable electronic device, method, and graphical user interface for displaying electronic lists and documents.” The patent is described as the “mother of all smartphone software patents” (Graziano). The patent shown is one of many patents covering many user interface designs for several key apps and services like emails, telephones, and browsers. “Apple now has a patent that covers a wide range of commonly used smartphone touchscreen user elements” (Moon). Figure 2, an illustration of a touch screen device, is another image submitted by Apple in its patent application for Patent Number 8223134B1.
Figure 2
Figure 3
References
Albouze, Jean-Francois. Generating Synthetic Group Selfies. 19 July 2018.
Azemi, Erin, et al. Eye Detection Methods and Devices.
Boudreau, Kevin J., et al. “Profiting from Digital Innovation: Patents, copyright and Performance.” Research Policy, vol. 51, no. 5, June 2022, p. 104477, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2022.104477.
Graziano, Dan. “Apple Wins ‘mother of All Smartphone Software Patents’ – Could Spell Trouble for Android.” Yahoo! News, Yahoo!, 2022, news.yahoo.com/apple-wins-mother-smartphone-software-patents-could-spell-201538837.html.
Forstall, Scott, et al. Portable Electronic Device, Method, and Graphical User Interface for Displaying Electronic Lists and Documents. 17 July 2012.
GreyB. “Apple Patents - Insights & Stats (Updated 2023).” Insights;Gate, 30 Apr. 2024, insights.greyb.com/apple-patents/.
Kwon, Seokbeom, and Alan C. Marco. “Can antitrust law enforcement spur innovation? antitrust regulation of patent consolidation and its impact on follow-on innovations.” Research Policy, vol. 50, no. 9, Nov. 2021, pp. 1–19, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2021.104295.
Moon, Brad. “Apple’s New Killer App: Its Smartphone Software Patent.” InvestorPlace, InvestorPlace, 9 Aug. 2012, investorplace.com/2012/07/apples-new-killer-app-its-smartphone-software-patent/.
O’Neill, Caitlin. “Apple Vision Pro: The Patents behind the Technology.” Minesoft, 21 Nov. 2023, minesoft.com/apple-vision-pro-the-patents-behind-the-technology/.
Rapacke, Andrew. “Apple, Software Patents & Social Distancing.” The Rapacke Law Group, 18 June 2020, arapackelaw.com/patents/softwaremobile-apps/apple-patent-social-distancing/.